相对定位与绝对定位
1、相对定位(是在标准文档流中的,没有脱标):就是微调元素位置的。让元素相对自己原来的位置,进行位置调整。
<div class="w"> <div class="box"></div> </div>css样式:
.w{
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
.box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
}代码演示:
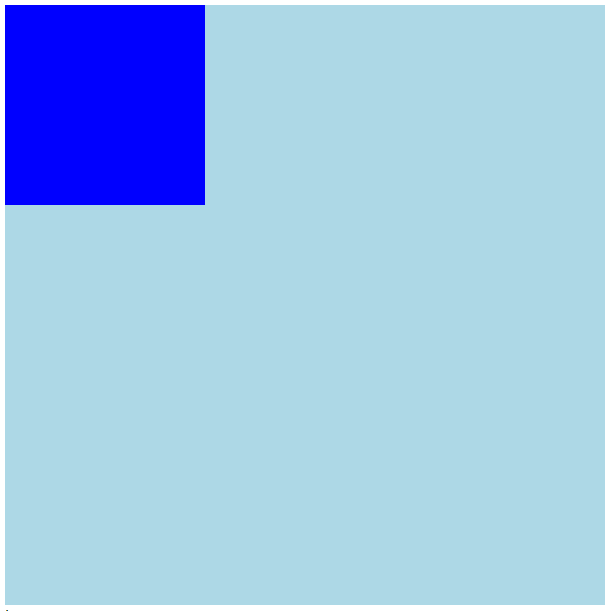
在box的css样式添加相对定位和定位值:CSS
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;代码演示:
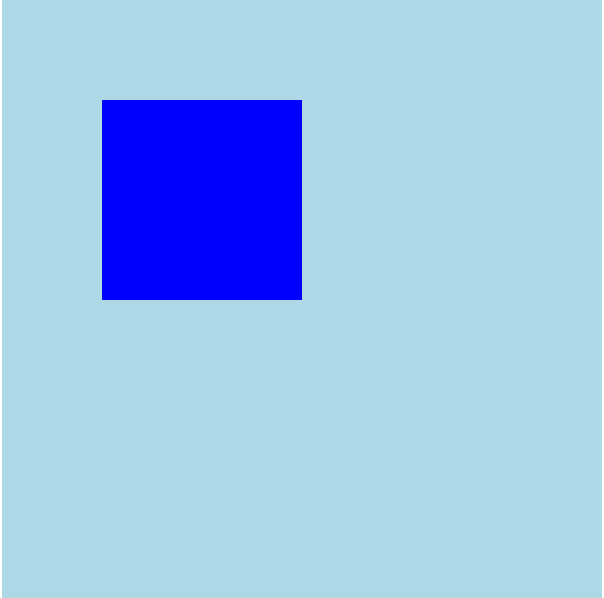
可以看出box的位置发生了变化,但这种变化是不脱标的,形影分离;他的内容虽然在其他地方显示,但相对定位之前的位置是不会被其他元素占领的
<div class="box"></div>
<div class="box1">'</div>css样式:
.box{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: blue;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
.box1{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: red;
}
<div class="box"></div>
<div class="box1">'</div>代码演示:
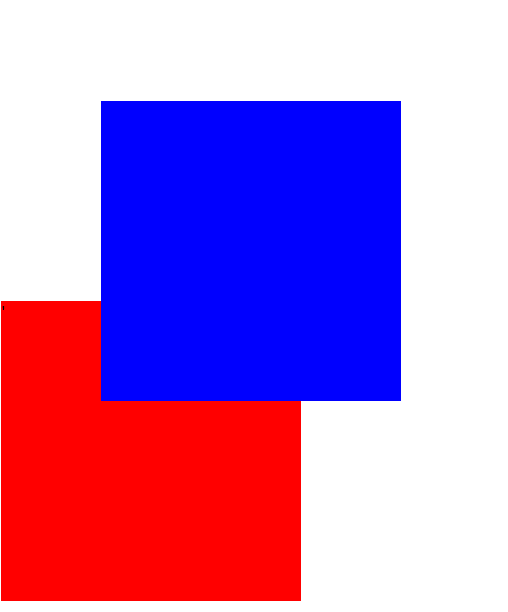
如果一个盒子在它相对定位的时候,如果有父元素,拿他的相对定位参考点是父元素的左上角,而非页面左上角
<div class="parent">
<div class="box2">
</div> </div>css样式:
.parent{
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
background-color:orange;
}
.box2{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #fff;
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}代码演示:

相对定位的用途
相对定位有坑,所以一般不用于做"压盖”效果。页面中,效果极小。就两个作用:
1)微调元素
2)做绝对定位的参考,"子绝父相"(做绝对定位的父亲)
2、绝对定位的盒子,是脱离标准文档流的。所以,所有的标准文档流的性质,绝对定位之后都不遵守了。
绝对定位之后,标签就不区分所谓的行内元素、块级元素了,不需要display:block;就可以设置宽、高了。
<div class="parent">
<div class="son son1"></div>
<div class="son son2"></div>
<div class="son son3"></div>
</div>css样式:
.parent{
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
background-color:orange;
position: relative;
}
.son{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
.son1{
background-color: lawngreen;
}
.son2{
background-color: red;
}
.son3{
background-color:blue;
}
代码演示:
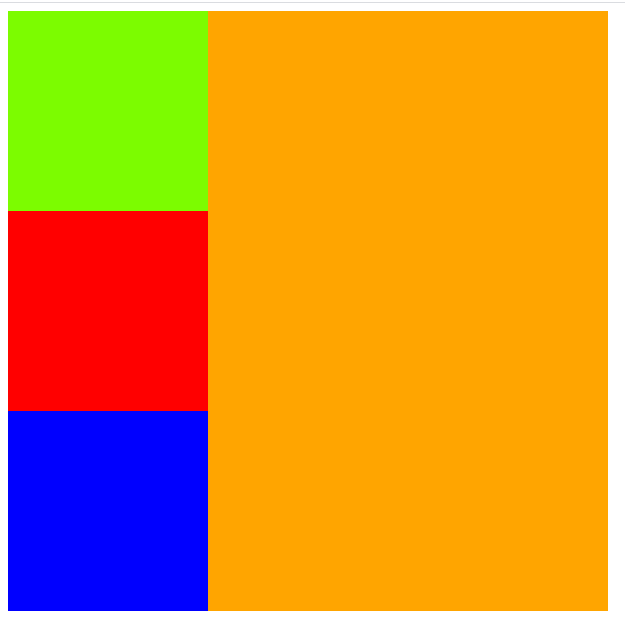
在此css样式基础上添加:
position: absolute;
left: 300px;
top: 300px;代码演示:
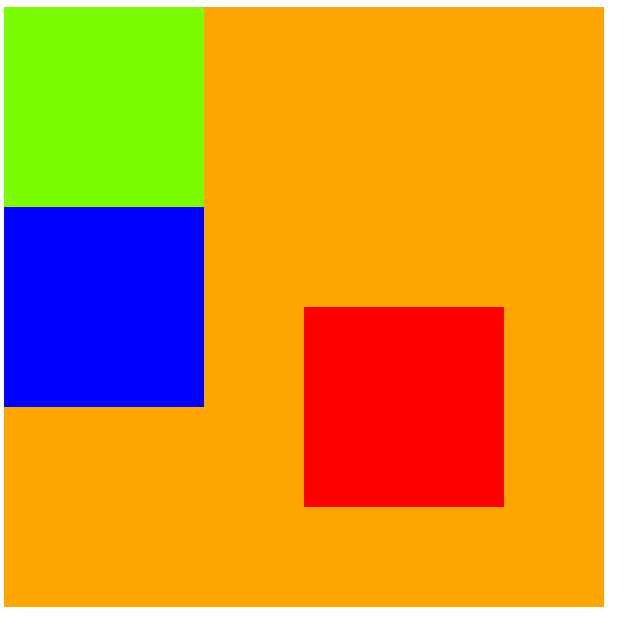
可以发现son2的位置发生了改变,而且son3取代了之前son2的位置,说明son2已经脱标
评论
匿名评论
隐私政策
你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果
